To perform an accurate RTK survey, you usually need a rover and a base that transmits the corrections in real-time. You can either use your own base or a remote one using a technology called NTRIP.
What Is NTRIP
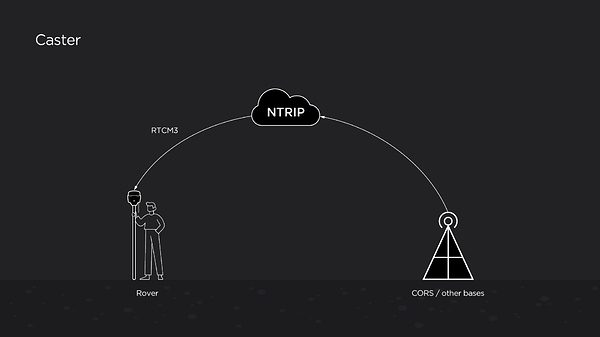
The Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol or NTRIP network was developed by the German Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy in 2004. NTRIP allows your rover to accept corrections over the Internet with no need for the second local receiver acting as a base.
NTRIP includes three main components of the system: base, caster, and client’s rover. Usually, in this case, there’s a stationary continuously operating reference station or CORS. The data is then sent to the NTRIP caster, where it is retransmitted through the Internet port to the client rover connected via a particular port and authorized.
How NTRIP works
Eventually, when using NTRIP, you receive all these corrections via a cellular modem installed in your rover.
How to Connect to NTRIP
To get access to the NTRIP network, you need to contact your local NTRIP service to create an account. Some of the NTRIP networks are run by states, some are free of charge, some of them are private and are pretty costly when it comes to the subscription fees.
There are free networks and services that provide NTRIP casters. One of them is rtk2go.com: a community where people stream their corrections from their bases. However, governmental or private corporate networks might be more reliable than the independent free ones.
In any case, once you’re registered, you’ll get a particular port and IP address to access and get authorized by the network. You’ll also need a username and password to log into the network.
Once you’ve completed the registration, you can use your credentials to connect your rover to the NTRIP network and receive connections. Check out our video tutorial on how to connect your Reach RS2 to NTRIP and work with correction data sent over a cellular modem.
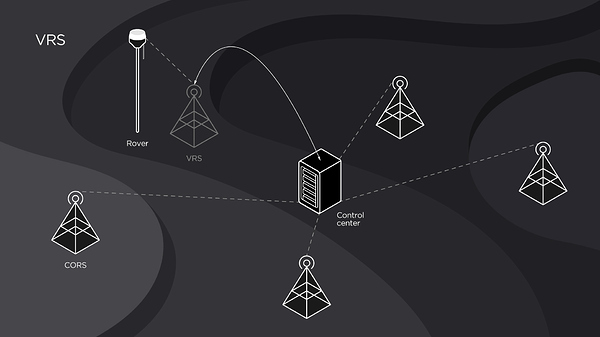
What Is VRS
If you’re working with NTRIP, there’s a good chance you’ll come across this term. VRS or Virtual Reference Station is a useful tool for long baselines.
The density of NTRIP bases and CORS can vary greatly from place to place. If the density of stations is enough, but you are too far from any of them, VRS helps you eliminate your baseline.
Say, you are 70 km away from the nearest station. When working in RTK mode, this baseline is quite long. To create a VRS, your rover sends data back to the NTRIP caster. NTRIP allows the uniting of the data from your rover and the data from dense NTRIP bases and models a virtual base next to you. Thus, your baseline will go from 70 km to 0 km.
The elimination of a baseline helps establish a fixed solution faster and keep it stable. VRS is especially useful for Reach RS+.
VRS allows you to eliminate the long baseline issue
Pros and Cons of Using NTRIP
NTRIP is a very useful method to implement when working in RTK. However, it has its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- High absolute accuracy. With corrections from NTRIP, you obtain high accuracy in your data.
- No need for a local base. You can work with just a rover and still perform an accurate survey.
- Fast fix. Internet connection to NTRIP helps you find the fix solution faster.
Disadvantages:
- Fees. Some NTRIP networks are private or for special governmental use, so you need to pay for using them. Sometimes it can get really expensive, so do your research beforehand.
- Being dependent on the Internet. NTRIP only works via the Internet, so you need the cellular network coverage to use it. That means if the surveying ground is beyond Internet coverage, NTRIP is unavailable.
Your decision on whether to use NTRIP or not mostly depends on your particular case and conditions you’re going to work in.
Reach Receivers for NTRIP Connection
Both Reach RS+ and Reach RS2 are suitable for working with NTRIP connection and receive the corrections via the Internet. Learn more and order Reach receivers in our online store.